High Mountain Health Radiology offers a range of imaging technology to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of injury and disease. These include:
 Bone Scanning, or Bone Densitometry Bone Scanning, or Bone Densitometry
 CT Scan, or CAT Scan CT Scan, or CAT Scan
 Whole Body Scan Whole Body Scan
 EchoCardiogram EchoCardiogram
 MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Nuclear Medicine Nuclear Medicine
 Ultrasound Ultrasound
 X-rays X-rays
These tests are used to diagnose men, women and children. In addition, High Mountain Health offers a range of tests that are specific to Womens needs. Click here for complete information on our Women's Radiology program.
Helpful Links
http://www.radiologyinfo.org/index.cfm?bhcp=1
Summary of Radiology Testing
 Bone Scan or Bone Densitometry measures mineral content in the bones. It involves an extremely small dose of radiation that determines your bone mineral density (BMD). It compares your measurements to a reference population based on your age, weight, sex and ethnic background. Physicians use this information to diagnose bone status and fracture risk. Low bone density is caused by osteoporosis, causing bones to become brittle. If detected, preventive therapy can be prescribed to slow or halt bone loss and, in some cases, reverse it. Bone Scan or Bone Densitometry measures mineral content in the bones. It involves an extremely small dose of radiation that determines your bone mineral density (BMD). It compares your measurements to a reference population based on your age, weight, sex and ethnic background. Physicians use this information to diagnose bone status and fracture risk. Low bone density is caused by osteoporosis, causing bones to become brittle. If detected, preventive therapy can be prescribed to slow or halt bone loss and, in some cases, reverse it.
Return to top of page
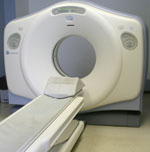  CT Scan is a radiographic technique that rotates multiple “cameras” around the patient and then uses a computer to assimilate multiple X-Ray images into a two-dimensional, cross-sectional view of the area being scanned. There is no pain or discomfort and scanning only takes a few minutes. CT Scanning is very quick and is helpful in rapid diagnosis of traumatic injuries and in guiding needle biopsies. CT Scan is a radiographic technique that rotates multiple “cameras” around the patient and then uses a computer to assimilate multiple X-Ray images into a two-dimensional, cross-sectional view of the area being scanned. There is no pain or discomfort and scanning only takes a few minutes. CT Scanning is very quick and is helpful in rapid diagnosis of traumatic injuries and in guiding needle biopsies.
Also known as CAT scans and Computed Tomography, CT scans can be taken of the entire body or of selected areas under study. Some of the scans offered at High Mountain Health are as follows:
 Whole Body Scan If you have a family disease or are over the age of 40, a whole body scan may be a valuable tool to monitor your health. Designed as an early detection system, it can help you prevent and treat medical problems before they become critical. The Total Body Scan consists of a screening of the coronary arteries, the lungs, the abdomen and pelvis. It should not replace other screening and diagnostic procedures that have been recommended to you, but it can be an extremely valuable supplement. Whole Body Scan If you have a family disease or are over the age of 40, a whole body scan may be a valuable tool to monitor your health. Designed as an early detection system, it can help you prevent and treat medical problems before they become critical. The Total Body Scan consists of a screening of the coronary arteries, the lungs, the abdomen and pelvis. It should not replace other screening and diagnostic procedures that have been recommended to you, but it can be an extremely valuable supplement.
o Aortic aneurysm and plaque in major abdominal vessels
o Chest and lung abnormalities, including lung cancer, pneumonia, lung fibrosis, hiatal hernia, pleural disease, mediastinal abnormalities and nodes. A majority of cancers found with this new CT technology can be cured in the early stages.
o Coronary Artery Disease. A scan can detect the amount of calcium in the walls of coronary arteries. It calculates the “calcium score,” which may serve as a predictor of future coronary events.
o Coronary Calcium Scoring
o Degenerative changes in the spine
o Kidney Disease or Kidney Cancer
o Ovarian and Pelvic Masses
o Osteoporosis
o Some growths, nodules or cancers in the liver, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, ovaries and uterus
o Some types of stones in the kidneys and gallbladder
o Virtual Colonography. This new test for colon cancer screening can detect polyps as small as one centimeter. An oral colonic cleaner is administered the day before the exam. Just before the study, air is instilled into the colon and then the scan is performed. The entire test takes about 20 minutes and actual scanning time is less than one minute. No sedation is required.
Return to top of page
  Echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart. It uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasounds) to image the heart and its surrounding areas.The images are then reviewed by the Radiologist. Echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart. It uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasounds) to image the heart and its surrounding areas.The images are then reviewed by the Radiologist.
Return to top of page
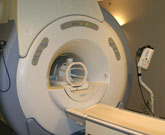
Resonance Imaging). An MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce a photo-quality image of the inner body. It is a safe and efficient means of diagnosing injury and disease. Its advantage is that it can lead to early detection and treatment of disease without surgery or biopsy. It is completely non-invasive and it provides digital images of the soft tissue of the body, including organs, muscles and tendons.
 MRI (Magnetic MRI (Magnetic
An MRI requires a patient to lie still, usually on their back for at least 15 minutes (and for some tests up to 45 minutes). Blankets and pillows are provided and every effort is made to keep you comfortable during the test. Some MRI exams require an injection of "Gadolinium," which is a contrast material that increases the visibility of body tissue in the MRI images.
Return to top of page
  Nuclear Medicine scans trace radioactive compounds through certain parts of the body to evaluate whether there is any abnormality in bone, liver, lungs, heart, brain, kidneys and the endocrine system. The test can take between 30 and 60 minutes, during which time the patient lies still. The procedure is very safe and the tracer material is usually eliminated by the body within 24 hours. Nuclear Medicine scans trace radioactive compounds through certain parts of the body to evaluate whether there is any abnormality in bone, liver, lungs, heart, brain, kidneys and the endocrine system. The test can take between 30 and 60 minutes, during which time the patient lies still. The procedure is very safe and the tracer material is usually eliminated by the body within 24 hours.
Return to top of page
 An Ultrasound consists of a series of high-frequency sound waves to form a photographic image of the area being scanned. It is commonly used to examine a developing fetus. It is also used to evaluate the structure and function of blood vessels, the pelvis, the abdominal system and breast tissue. An Ultrasound consists of a series of high-frequency sound waves to form a photographic image of the area being scanned. It is commonly used to examine a developing fetus. It is also used to evaluate the structure and function of blood vessels, the pelvis, the abdominal system and breast tissue.
Return to top of page
 X-Rays use small amounts of radiation that pass through the selected area of the body to capture an image on photographic film. X-rays are useful to evaluate the chest and musculoskeletal system. X-Rays use small amounts of radiation that pass through the selected area of the body to capture an image on photographic film. X-rays are useful to evaluate the chest and musculoskeletal system.
Return to top of page

The medical support team of High Mountain Health Radiology
|


 We offer a full range of diagnostic services and the highest quality of care by doctors who are certified to perform your tests and interpret the results of your imaging on the same day the test is performed.
We offer a full range of diagnostic services and the highest quality of care by doctors who are certified to perform your tests and interpret the results of your imaging on the same day the test is performed.







